Summary
The article explores two key data-migration strategies—Big Bang (everything moved in one go) and Gradual/Phased (chunks moved over time)—and lays out the advantages and risks of each. It helps organizations decide which approach fits them best by considering factors like scale, downtime tolerance, risk, and complexity.
Data migration is inevitable for almost any business looking to upgrade its systems and adopt new technologies. Whether you’re moving to a cloud-based platform, implementing a new software solution, or consolidating databases, the way you handle data migration can make or break the success of your project. With so much at stake, including possible downtimes, future data integrity, and operational continuity, choosing the right migration strategy is no small feat.
Here, the two most common approaches are Big Bang and Gradual Data Migration. The Big Bang method is like a high-stakes, all-or-nothing move. In this case, developers rely on a single, sweeping transition that happens in one go. Gradual Migration is a more measured, step-by-step process, allowing businesses to migrate data in phases while maintaining operations. Today, we’ll consider how choosing one of these approaches can work better for your business depending on various factors.
When Data Migration Is Necessary?
Data migration may be required in many various cases due to technological advancements, operational inefficiency, or compliance requirements. Recognizing the right time for data migration can help companies save money, avoid security risks, and overcome system failures more efficiently. Let’s consider the most common situations, when data migration is necessary:
- Transition to Modern Systems. At some point, old and reliable software may become outdated and slow. To reap the benefits of cloud computing, AI-driven analytics, or automation, businesses can consider migrating their data to more advanced platforms as a part of their software modernization strategy;
- Mergers, Acquisitions, and Business Restructuring. Here, integrating disparate IT systems is required for future unified operations. Data migration ensures that all entities involved can consolidate their databases, eliminate redundancies, and create a seamless flow of information across departments. Similarly, companies undergoing restructuring may need to transfer data between different business units or reorganized systems;
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements. Industries such as healthcare, finance, and logistics are subject to evolving regulations that dictate how data should be stored, accessed, and secured. Businesses often need to migrate data to compliant systems that meet regulatory standards;
- System Performance and Scalability Issues. When an organization experiences slow system performance due to excessive data load, cloud data migration can improve efficiency;
- Disaster Recovery and Security Considerations. Cloud data migration is often necessary as part of a disaster recovery strategy. Businesses looking to safeguard their information against cyber threats, hardware failures, or natural disasters may migrate data to secure, cloud-based backups or secondary data centers.
Read Also Top List of Signs that Your Legacy Software Needs Modernization
Big Bang Data Migration: When Speed Outweighs Risk
Big Bang data migration is a high-speed, all-at-once approach where an entire data transfer occurs within a short, predefined timeframe. This method is often implemented during scheduled downtimes, making it a suitable option for businesses that can afford temporary service interruptions. However, while it offers a faster transition, it also carries certain database migration risks and challenges.
In a Big Bang migration, all data is extracted from the old system, transformed if necessary, and then loaded into the new system in a single event. Therefore, this approach requires extensive preparation, including backups, data validation, and testing to minimize errors and downtime. The transition is typically executed over a weekend or holiday to reduce business disruption.
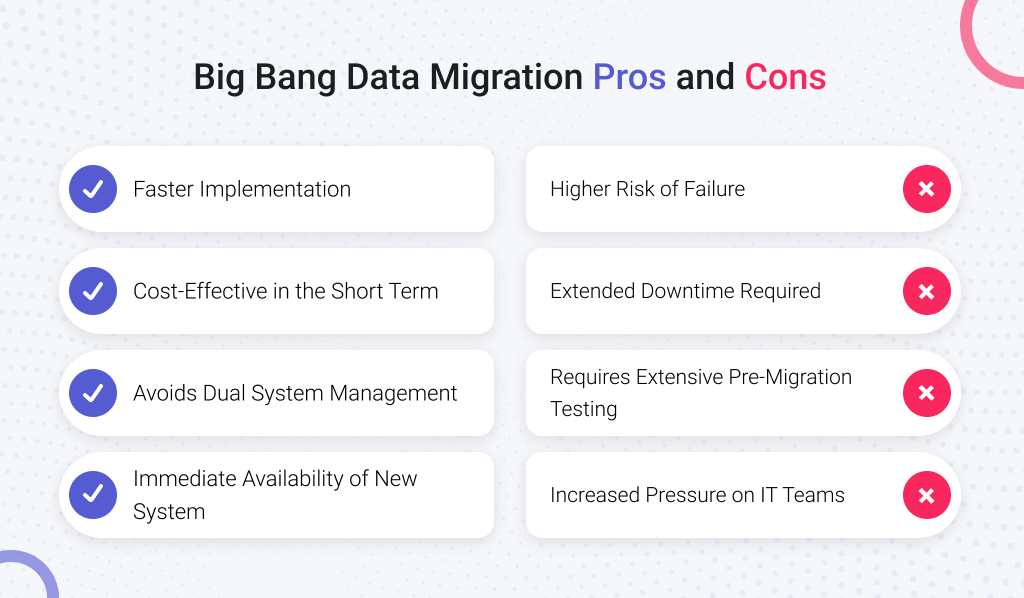
Advantages of Big Bang Migration
- Faster Implementation. The entire migration is completed in one go, reducing the prolonged coexistence of old and new systems;
- Cost-Effective in the Short Term. Since the migration happens all at once, businesses may save on operational costs associated with running parallel systems;
- Avoids Dual System Management. Organizations don’t have to maintain and synchronize two systems over an extended period;
- Immediate Availability of New System. Once the migration is complete, users can start working with the upgraded platform without waiting for gradual phases.
Disadvantages of Big Bang Migration
- Higher Risk of Failure. If issues arise during the migration, the entire system could face data loss, corruption, or unexpected downtime;
- Extended Downtime Required. Businesses that operate 24/7 may struggle to find a suitable time window for such a transition;
- Requires Extensive Pre-Migration Testing. To minimize errors, thorough planning and rigorous testing must be conducted before execution;
- Increased Pressure on IT Teams. Since everything must go smoothly within a short timeframe, IT teams must be well-prepared to handle unexpected failures.
When to Choose Big Bang Data Migration
While Big Bang migration may seem like a high-risk, high-reward strategy, there are specific scenarios where it shines as the best option. Let’s take a closer look at when this approach makes the most sense for your business:
- Small-Scale Operations. If your business is relatively small with limited data and straightforward systems, a Big Bang migration can be a practical choice. Smaller organizations often have fewer dependencies and less complexity, making it easier to execute a one-time transition without major disruptions;
- Tight Deadlines. When time is of the essence, the Big Bang approach can be a lifesaver. Since the entire migration happens in one go, it’s faster than a phased approach. This is particularly useful for businesses that need to launch a new product fast or align with a specific business milestone;
- Limited Resources for Long-Term Projects. If your team lacks the resources or bandwidth to manage a prolonged migration process, the Big Bang approach can be more efficient. It consolidates the effort into a single, focused event, reducing the need for ongoing coordination and maintenance;
- Clear Cut-Over Point. For businesses that want a clean break from their old system, Big Bang data migration offers a definitive switch. Once the migration is complete, the old system is retired, and the new system takes over entirely. This can be appealing for organizations looking to fully embrace a new platform without lingering ties to legacy systems.
Example: A small accounting firm with 10 employees that uses outdated tax preparation software lacking modern features like cloud storage support, real-time collaboration, and automated tax calculations. With tax season approaching, the firm decides to switch to a new, cloud-based tax software. A relatively small dataset, simple architecture, tight deadlines, and full one-shot transition to a new system with no intent to work with the old one can be the reasons to prefer Big Bang data migration.
Gradual Data Migration: A Phased Approach for Complex Systems
Gradual data migration, also known as phased migration, is a step-by-step approach where data is transferred in stages over a defined period. Unlike Big Bang data migration, this method allows businesses to continue operations with minimal disruptions, making it an attractive option for organizations that require high availability.
In a gradual migration strategy, data is segmented and transferred in phases, often based on business priorities, departments, or system modules. This process involves running the old and new systems in parallel, allowing for real-time software testing, validation, and adjustments along the way. Companies can monitor the performance of each migrated component and address any issues before proceeding to the next phase.
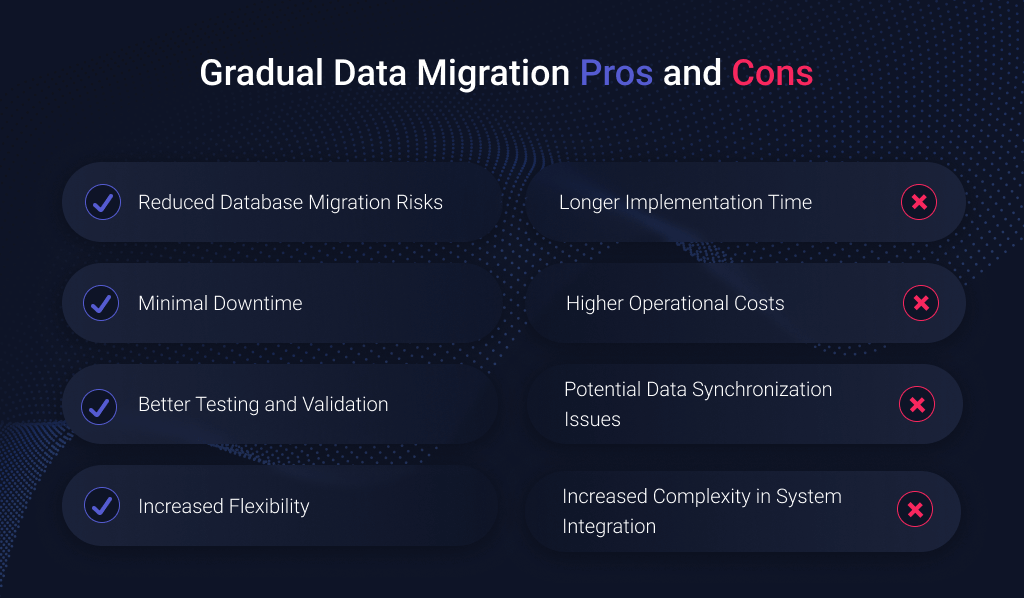
Advantages of Gradual Migration
- Reduced Database Migration Risks. Since data migration occurs in small increments, any errors or failures can be detected and corrected without impacting the entire system;
- Minimal Downtime. Businesses can continue running operations while data is gradually transferred;
- Better Testing and Validation. Teams can test and optimize each phase, ensuring smoother integration;
- Increased Flexibility. Adjustments can be made during the migration process, reducing unforeseen complications.
Disadvantages of Gradual Migration
- Longer Implementation Time. The phased approach extends the data migration timeline, requiring patience and ongoing management;
- Higher Operational Costs. Running two systems in parallel can be resource-intensive;
- Potential Data Synchronization Issues. Keeping old and new systems aligned requires careful planning to prevent inconsistencies;
- Increased Complexity in System Integration. Managing dependencies between old and new systems can introduce technical challenges, requiring additional effort to ensure seamless communication and functionality.
When to Choose Gradual Data Migration
Gradual data migration is like running a marathon. It’s a steady, phased process that prioritizes precision and risk management over speed. While it may take longer to complete, this approach is often the safer and more practical choice for businesses with complex systems or high-stakes operations. Here’s when Gradual Migration makes the most sense for your business:
- Large-Scale Enterprises. For large organizations with vast amounts of data and multiple interconnected systems, a gradual approach is often the only feasible option. It allows businesses to tackle the migration in manageable chunks, reducing the risk of overwhelming their teams or systems;
- Mission-Critical Systems. If your business relies on systems that cannot afford extended downtime, such as healthcare, finance, or e-commerce platforms, gradual migration is the way to go. By migrating in phases, you can ensure that critical operations remain functional throughout the process;
- Limited Risk Tolerance. If your business cannot afford the potential fallout of a failed migration, the gradual approach provides a safety net. Issues can be identified and resolved in smaller phases, minimizing the impact on overall operations;
- Need for Continuous Testing and Feedback. Gradual migration allows businesses to test each phase of the migration and gather feedback before moving on to the next. This iterative process ensures that the new system is fully functional and meets business requirements before the final cutover;
- Regulatory or Compliance Requirements. For industries with strict regulatory requirements, such as healthcare or finance, gradual data migration provides the opportunity to ensure compliance at every stage. This reduces the risk of non-compliance penalties and ensures data integrity throughout the process.
Example: A medium-sized e-commerce business with 50 employees that uses an outdated order management system (OMS) unable to handle growing sales volume or integrate with the new warehouse management software. To improve efficiency, the company decides to migrate to a modern, cloud-based OMS. Large datasets (customer orders, inventory, and shipping details), 24/7 operations with no possibility of downtimes, company’s requirement to minimize risks and ensure painless integration with other tools are core factors to choose gradual migration.
Big Bang vs. Gradual Data Migration: Key Differences
Choosing the right data migration approach depends on your business needs, risk tolerance, and operational constraints. The table below highlights the main differences between Big Bang and Gradual Migration to help you decide which method best suits your organization.
| Feature | Big Bang Migration | Gradual Migration |
| Implementation Speed | Fast, completed in one go | Slow, completed in phases |
| Risk Level | High: any failure affects the whole system | Lower: issues can be fixed in stages |
| Business Downtime | Significant downtime required | Minimal to no downtime |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower short-term costs | Potentially higher due to parallel systems |
| Testing Flexibility | Limited, must be done before migration | Ongoing testing possible |
| Best Fit For | Small- to mid-sized businesses, companies that can afford downtime | Large enterprises, industries requiring continuous operation |
Use Case Example: Modernizing a Financial CRM
As an example, let’s consider how we performed data migration for a financial services company, specializing in wealth management, retirement planning, and investment strategies.
Our client’s CRM system was beginning to show its age. The legacy app lacked integration with modern tools, required extensive manual data entry, and offered limited analytics capabilities. The company needed a modern solution that could:
- Streamline operations by reducing manual work and automating repetitive tasks;
- Integrate seamlessly with existing financial software, email systems, and customer support tools;
- Provide advanced analytics to better understand client behavior and preferences.
Why Data Migration Was Necessary
The existing CRM system housed years of valuable client data, including financial records, investment histories, and customer interactions. However, the outdated database structure and lack of integration made it difficult to leverage this data effectively. Data migration was essential to:
- Eliminate inefficiencies caused by manual processes and outdated workflows;
- Unlock the full potential of client data through advanced analytics and real-time insights;
- Future-proof the business by adopting scalable, cloud-based technologies.
Our Solution: Gradual Data Migration and System Modernization
We recommended a Gradual Data Migration approach due to the following reasons:
- It minimized disruption to the company’s operations, ensuring business continuity during the transition;
- It allowed for thorough testing and validation at each phase, reducing the risk of errors;
- It provided the flexibility to address complex dependencies and integrate with multiple systems seamlessly.
Here’s how we did it:
1. Assessment and Planning. We began with developing our cloud migration strategy. Our team evaluated the existing system’s architecture, database structure, and dependencies. This helped us identify which data and features were critical to migrate and which could be updated or replaced;
2. Phased Data Migration:
- Phase 1: We migrated non-critical data, such as archived client records, to test the new system and ensure data integrity;
- Phase 2: Active client data and transaction histories were moved to the modern CRM, enabling real-time access and analysis;
- Phase 3: The new system was integrated with the company’s financial software, email systems, and customer support tools, creating a unified platform for all operations.
3. Technology Stack Modernization:
- The backend, originally written in PHP, was updated to a modern version, and inefficient code was refactored;
- The frontend was rebuilt using ReactJS, chosen for its flexibility and component-based architecture, which allowed for reusable and scalable code;
- The database structure was optimized to handle exponential data growth, with cloud storage solutions improving processing speed and reliability.
Read Also From Old to Gold: Transforming Legacy Systems with Modernization Techniques (with Real Examples)
The Value Delivered
The modernized CRM system transformed the way the company managed client relationships and operational workflows. Key outcomes included:
- Enhanced Customer Relationship Management. The new system provided a 360-degree view of client interactions, enabling personalized services and faster response times;
- Stronger Client Loyalty. With advanced analytics, the company gained deeper insights into client preferences, helping them build stronger, more meaningful relationships;
- Improved Operational Efficiency. Automation and seamless integration reduced manual data entry, minimized errors, and saved time, allowing employees to focus on higher-value tasks;
- Scalability for Future Growth. The modern, cloud-based architecture ensures the system can handle increasing data volumes and evolving business needs.
Conclusions
Choosing between big bang and gradual data migration is not a decision to be taken lightly. Each approach has its own strengths and challenges, and the right choice depends on your business’s unique needs, size, and risk tolerance. Whether you’re looking for a swift, all-at-once transition or a cautious, phased approach, the key to success lies in careful planning, thorough testing, and a clear understanding of your goals.
Ready to take the next step? Contact us to discuss your data migration needs and discover how we can help your business thrive in the digital age.